Health Knowledge: Types of Stroke in Malaysia
A stroke is a condition whereby the blood vessel to the brain is blocked or ruptured. This causes insufficient oxygen content in the brain, damaging the brain tissue. When a part of the brain tissue dies, the function of that tissue is lost.
When a person suffers from a stroke, prompt treatment is crucial to reduce brain damage and other complications. Otherwise, it can cause severe disability.
In Malaysia, stroke has become a public health concern as it can occur in anyone. Additionally, statistics show that cerebrovascular disease such as stroke is the third principal cause of death among Malaysians. It accounts for 8% of the more than 100,000 medically-certified deaths in the year 2019.
In 2001, The World Health Organisation (WHO) estimated that there were over 20.5 million stroke cases worldwide. Today, the number of deaths due to stroke accounts for five times that, along with other non-communicable diseases.
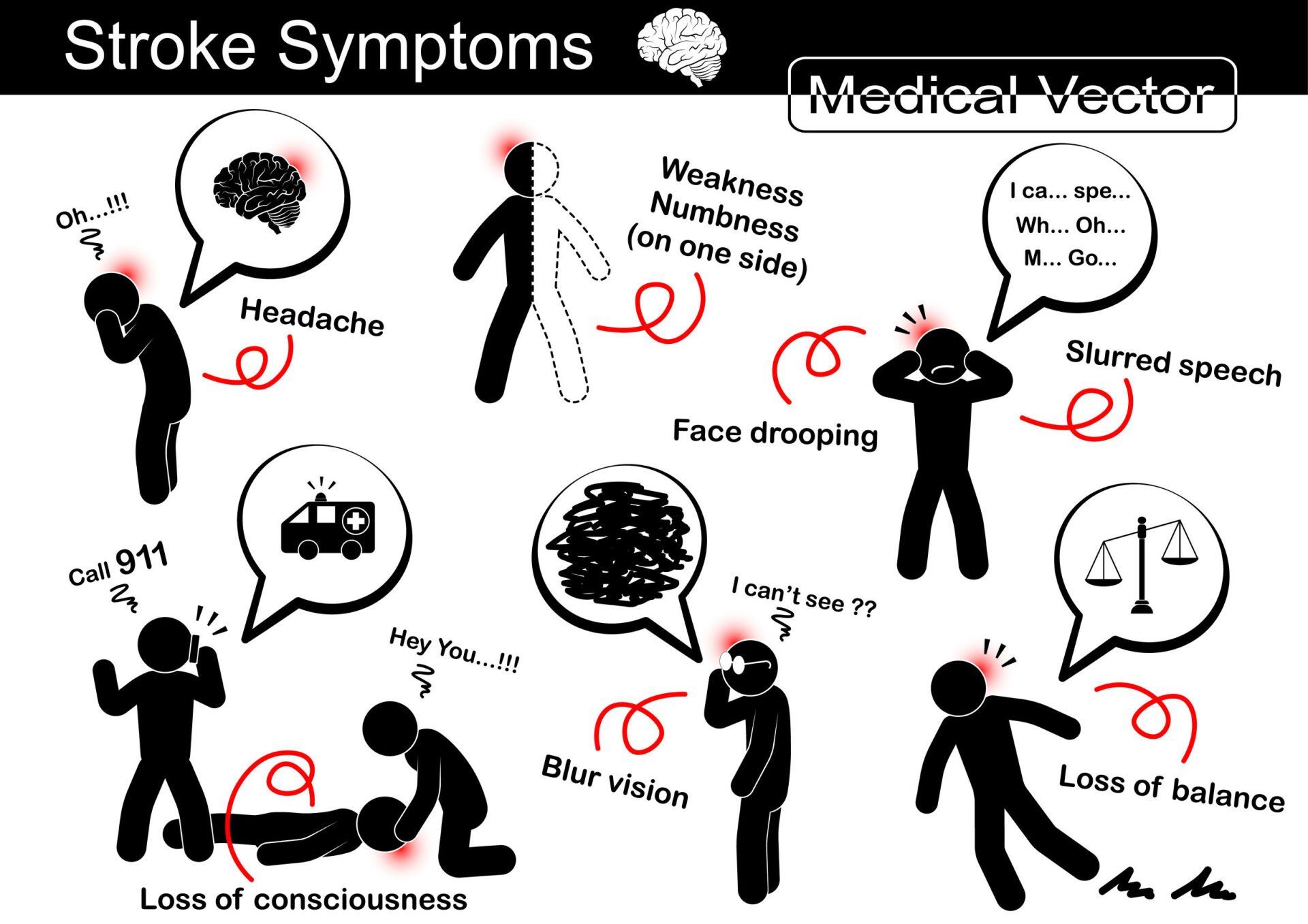
Symptoms of stroke
If you or someone you know shows signs of having a stroke, pay attention to them when the symptoms appear. Some treatments are only effective when given soon after a stroke. The signs and symptoms of a stroke include:
- Trouble speaking and understanding – Slurred words or difficulty understanding what other people say.
- Paralysis or numbness on the face, arm, or leg – Stroke often affects one side of the body, causing sudden numbness, weakness, or paralysis on one side of the face, arm, or leg.
- Problems seeing in one or both eyes – Sudden experience of blurred or blackened vision in one or both eyes.
- Headache – Sudden severe headache with no obvious cause.
- Trouble walking – Sudden trouble walking or loss of balance and coordination. May be accompanied by dizziness.
Causes of stroke
The blood supplies oxygen to the brain by travelling through blood vessels known as arteries. When any of the arteries to the brain is blocked, it causes an ischaemic stroke to occur. If the artery to the brain is ruptured, it can cause haemorrhagic stroke.
Types of stroke
Generally, there are two causes of stroke – a blocked artery or ruptured blood vessel. In some cases, there may be a temporary disruption of the blood flow to the brain, known as a transient ischaemic attack (TIA). Here are the three types of stroke – ischaemic stroke, haemorrhagic stroke, and transient ischaemic attack.
1. Ischaemic stroke
An artery blockage is often the cause of an ischaemic stroke. This happens when an artery to the brain becomes narrow or experiences a blockage, depriving the brain of blood and oxygen. As a result, the brain tissue dies and stops functioning. The blockage is often associated with fatty build-ups or blood clots, which over time cause the blood vessel to become narrow.
2. Haemorrhagic stroke
When a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, it leaks and spills blood into brain tissue, causing the affected brain cells to stop working. Brain haemorrhages can result from a variety of conditions such as uncontrolled high blood pressure, trauma, protein deposits on blood vessel walls, overtreatment with anticoagulants, bulges at weak spots in blood vessel walls, and ischaemic stroke.
3. Transient ischaemic attack (TIA)
Often referred to as a ‘mini-stroke’, a transient ischaemic attack is a short-lived stroke (within 24 hours) which improves spontaneously. It’s typically caused by a temporary decrease in blood supply to a part of the brain. Like an ischaemic stroke, a TIA occurs when there’s a blockage in the blood vessels to the brain. It can also be a warning sign of a future stroke.
Between the year 2009 and 2016, ischaemic stroke accounts for 76% of the registered stroke cases in Malaysia while haemorrhagic stroke accounts for 17% of the cases. TIA accounts for 2% of the registered cases.
Regardless of how healthy you are, there’s no knowing when a stroke can happen to you. It can be due to various factors such as lifestyle habits, medical conditions, age, sex, and family history.
Stroke Treatment and Prevention
Now that you've learnt about the symptoms and types of stroke, knowing your risk factors, following your doctor’s recommendations, and adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial to prevent future stroke. This includes:
- - Getting admitted to the hospital after suffering from a stroke to understand the cause and extent of possible brain damage.
- - Undergoing an operation when needed to stop the bleeding or remove the blood clot.
- - Managing lifestyle habits to reduce risks of stroke.
- - Undertake rehabilitation to improve life quality after a stroke.
The effects of a stroke in Malaysia can be overwhelming, but in some cases, may cause severe and permanent disabilities. That said, Well Rehab provides several types of rehabilitation which can be customised based on your needs and conditions.
For more information about our therapies or services, you may contact us at +60 12 512 8487 or email wellrehabmanagement@gmail.com.




